Top ML Frameworks for Job Seekers
Compare Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch, gradient-boosting and LLM frameworks, plus the complementary skills employers want to make your ML resume stand out.

Machine learning skills are non-negotiable for landing top roles like ML Engineer, Data Scientist, or AI Engineer in 2026. Employers prioritize candidates who know how to build, deploy, and scale models efficiently. Mastering the right frameworks can help you stand out, optimize your resume for Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), and increase your chances of interview callbacks by up to 30%.
Here’s a quick overview of the top ML frameworks you need to know:
- Scikit-learn: Best for classical machine learning tasks like regression and clustering. Ideal for structured data projects in industries like finance and healthcare.
- TensorFlow: Perfect for deep learning and large-scale production. Used for neural networks, image recognition, and NLP.
- PyTorch: A favorite for research and experimentation, especially in NLP, computer vision, and AI innovation.
- Gradient Boosting Libraries (XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost): Essential for structured data modeling in finance and insurance.
- LLM and GenAI Frameworks (Hugging Face Transformers, LangChain): Key for building applications with large language models, like chatbots and generative AI systems.
Quick Tip: Use AI-powered tools like scale.jobs to tailor your resume with the right framework keywords and boost your chances of passing ATS screenings.
Below, we’ll break down how each framework aligns with career goals, industry demand, and complementary tools to help you succeed.
1. Scikit-learn
Career Relevance
Scikit-learn is the go-to framework for classical machine learning, making it a must-know for roles like Data Scientist, Machine Learning Engineer, or Risk Analyst. While deep learning frameworks dominate neural network tasks, Scikit-learn shines in traditional machine learning areas like regression, classification, and clustering - core components of most business applications in 2026. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), fintech companies, and forecasting systems heavily rely on professionals skilled in this framework.
What sets Scikit-learn apart is its ability to handle the entire machine learning pipeline. From data preprocessing to feature scaling and model evaluation, it simplifies complex workflows. Employers now prioritize candidates who understand advanced features like Pipeline and GridSearchCV - tools that streamline and optimize systems for real-world use. For structured data projects in industries like finance, insurance, and healthcare, Scikit-learn remains a cornerstone technology, driving its widespread adoption by leading organizations.
Industry Demand
Scikit-learn's practical capabilities make it highly sought after in the job market. Its tools are integral to many business operations. For instance, in January 2025, Spotify was noted for using Scikit-learn in its music recommendation system, analyzing user behavior and song attributes to deliver personalized track suggestions. This isn't just a niche application - it's a large-scale, consumer-facing system that highlights the framework's dependability. According to Kaggle surveys, Scikit-learn continues to be the most popular machine learning framework, especially for tabular data, which dominates sectors like finance and insurance.
"If you don't need deep learning, Scikit-learn is your best friend. It's great for classic machine-learning tasks like classification, regression, and clustering." - Python Central
Learning Curve
One of Scikit-learn's standout features is its simplicity. The framework is easier to learn compared to deep learning alternatives, thanks to its clean syntax and detailed documentation. With just a few lines of code, you can transform raw data into a trained model, making it an excellent choice for beginners and experienced professionals alike.
Complementary Skills/Tools
To maximize your job readiness in 2026, combine Scikit-learn with NumPy and pandas for data manipulation - both are foundational libraries that Scikit-learn builds upon. Expanding your skill set to include XGBoost or LightGBM is also wise, as these gradient boosting libraries often outperform standard Scikit-learn models on tabular datasets. For deployment, learning FastAPI can help you turn your models into production-ready APIs. Additionally, integrating SHAP for model explainability is crucial, especially in regulated industries where transparency is key.
2. TensorFlow
Career Relevance
TensorFlow is a powerhouse when it comes to deep learning and large-scale production. If you're eyeing roles like Deep Learning Engineer, AI Scientist, or Machine Learning Infrastructure Engineer, this framework should be on your radar. Unlike Scikit-learn, which focuses on traditional machine learning techniques, TensorFlow shines in building neural networks - whether it's CNNs for image recognition, RNNs for time series analysis, or Transformers for natural language processing.
One of TensorFlow's standout features is its ability to scale for production. Its distributed computing capabilities make it ideal for handling real-world, enterprise-grade projects that require multiple GPUs or TPUs. Employers value this scalability, especially as they increasingly emphasize not just creating accurate models but managing the entire machine learning lifecycle - from training to deployment and monitoring. TensorFlow’s integration with Keras adds another layer of usability, offering a high-level API that simplifies building complex models without diving too deep into low-level code. If you've already mastered classical machine learning tools like Scikit-learn, TensorFlow is the natural next step to advance your deep learning expertise.
Industry Demand
TensorFlow has become a go-to framework for enterprises. Developed by Google, it's the backbone of many critical systems across top tech companies. For example, Google Translate relies on TensorFlow to enhance its language models, improving both speed and accuracy. Amazon uses it for recommendation systems and demand forecasting, supporting its massive logistics operations. Other major players like Airbnb, Twitter, NASA, AstraZeneca, and TikTok UK also use TensorFlow for their production machine learning needs.
"If you need a framework that can handle large-scale deep-learning projects, this is the one." - Python Central
Its versatility is another advantage. TensorFlow can be deployed across mobile devices (via TensorFlow Lite), web platforms (TensorFlow.js), and cloud environments (with seamless Google Cloud integration). According to a 2021 Stack Overflow survey, TensorFlow was the most used AI/ML framework, with 21.37% of developers expressing interest in learning it. Expert reviews for 2025/2026 consistently rate it 5/5 for Performance, Scalability, and Community Support.
Learning Curve
Learning TensorFlow can be a bit challenging compared to Scikit-learn, but the rewards are worth it. To get the most out of it, you'll need a strong foundation in Python and a clear understanding of deep learning concepts. Thankfully, TensorFlow's integration with Keras makes the initial learning phase more manageable. You can start experimenting with models quickly using Keras before delving into TensorFlow's more advanced, lower-level functionalities.
Complementary Skills/Tools
To stand out in the job market, consider pairing TensorFlow expertise with additional tools and skills. For MLOps, tools like MLflow and DVC are invaluable. Proficiency in containerization platforms like Docker and Kubernetes is also highly sought after. API frameworks such as FastAPI and Flask can help you deploy models effectively, while optimization tools like ONNX and TensorRT are essential for edge deployment. Additionally, explainability tools like SHAP and LIME are becoming increasingly important, especially in industries like finance and healthcare where transparency is critical. Mastering these complementary skills will give you a competitive edge in securing deep learning roles.
3. PyTorch
Career Relevance
PyTorch is more than just another machine learning framework - it’s a key to unlocking career opportunities in AI research, deep learning engineering, and cutting-edge product development. Known for its dynamic "define-by-run" computational graph, PyTorch allows real-time model modifications, making it a favorite among AI researchers. This flexibility is invaluable for creating innovative solutions, especially in fast-evolving fields.
One of PyTorch's standout features is its Pythonic design. Its API follows standard Python conventions, making it intuitive and easy to use for developers already familiar with Python. This simplicity doesn’t come at the cost of capability - PyTorch shines in areas like Natural Language Processing (NLP), computer vision, audio processing, and Large Language Models (LLMs). Careers that frequently demand PyTorch expertise include roles like Deep Learning Engineer, AI Scientist, Research Scientist, and Machine Learning Engineer, especially in positions focused on innovation and advanced problem-solving.
Industry Demand
PyTorch has grown beyond its academic roots to become a staple in production environments. By 2024, the number of organizations using PyTorch worldwide had doubled, and contributions to its development increased by an impressive 133%. Major players like Tesla rely on PyTorch for training AI models used in self-driving cars, leveraging its adaptability to handle complex, real-world scenarios.
"PyTorch's API is simpler and more Pythonic, making it easier to learn for developers who are familiar with Python." - Python Central
In terms of usability, PyTorch is rated as "Easy", compared to TensorFlow's "Moderate" rating. This accessibility, combined with its growing adoption in production systems, makes it a powerful asset for job seekers aiming to stay competitive in 2026 and beyond.
Learning Curve
If you’re already comfortable with Python, PyTorch is one of the easiest frameworks to pick up. Its seamless integration with tools like NumPy, Numba, and Cython means your existing Python skills will directly apply. To get started, you’ll need a solid grasp of deep learning concepts like CNNs, RNNs, and Transformers, but the framework itself won’t be a roadblock. Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can dive into specialized tools like PyTorch Lightning, which simplifies training workflows, and Torchvision, designed for computer vision tasks.
Complementary Skills/Tools
To maximize PyTorch's potential, pair it with tools that enhance model development and deployment. For MLOps, consider using MLflow for model tracking and DVC for data versioning. Deployment frameworks like FastAPI or Flask are excellent for building APIs, while Docker is essential for containerization. For optimized inference across hardware platforms, ONNX (Open Neural Network Exchange) is a must-have.
As generative AI continues to dominate, tools like Hugging Face Transformers and LangChain are invaluable for working with LLMs. Additionally, explainability tools such as SHAP and LIME are becoming increasingly important, particularly in regulated industries like finance and healthcare. By combining PyTorch with these complementary tools, you’ll have a well-rounded skill set that connects seamlessly with the broader machine learning ecosystem.
4. Gradient Boosting Libraries (XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost)
Career Relevance
If you’re working with structured data - think spreadsheets, databases, or CSV files - libraries like XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost are must-haves. These tools consistently outperform deep learning methods when it comes to tabular data, making them key for industries like finance, insurance, and actuarial tech. Companies such as Aviva, Barclays, and Wise are actively on the lookout for professionals skilled in building production-ready models with these libraries.
Roles like Risk Analyst, Applied Machine Learning Engineer, and Data Scientist rely heavily on these tools. Unlike research-driven positions that might focus on PyTorch or TensorFlow, these roles are all about solving practical business problems - fraud detection, credit scoring, insurance pricing, and time-series forecasting. By 2026, employers are prioritizing professionals who can deploy models that meet strict demands for latency, cost efficiency, and explainability. Mastering these libraries not only sharpens your production skills but also makes you a valuable asset who can deliver results that matter.
Industry Demand
The numbers speak for themselves: AI technologies in global banking could generate up to $1 trillion in additional value annually, with gradient boosting libraries driving much of this transformation. While large language models dominate headlines, these frameworks remain the go-to solution for tabular data in sectors like fintech and insurance.
"Employers aren't just hiring based on Kaggle scores. They want production-ready ML skills." – Machine Learning Jobs Skills Radar 2026
Why do these tools stand out? Their precision in predictive modeling directly impacts the bottom line. Whether it’s a bank forecasting risk or an insurance company setting policy prices, gradient boosting delivers results that deep learning often struggles to achieve with structured datasets. This proven track record makes these libraries indispensable, offering a manageable learning curve and immediate applicability.
Learning Curve
If you’re already comfortable with Python and use libraries like pandas and NumPy, picking up XGBoost, LightGBM, or CatBoost is quite straightforward. These libraries share similar APIs, so once you’ve learned one, the others become easier to understand. The real challenge lies in feature engineering, a critical step for extracting maximum performance from these tools.
You’ll also need to dive into hyperparameter tuning and early stopping techniques to avoid overfitting. These practical skills are what separate casual users from professionals who can deploy models in production environments. While the learning curve is moderate, the payoff is quick - you can start applying these skills to real-world projects within weeks.
Complementary Skills/Tools
To truly stand out in 2026, combine your expertise in these libraries with tools that enhance model explainability, like SHAP and LIME, as well as deployment and tracking tools such as FastAPI, Flask, Docker, MLflow, and DVC. Proficiency in SQL is also essential for efficient feature extraction.
As more companies emphasize monitoring models in production, familiarity with tools like Prometheus and Grafana for detecting model drift can give you an edge over other candidates. These complementary skills not only boost your technical toolkit but also position you as someone ready for the demands of modern machine learning workflows.
AI Engineer Roadmap | How I'd Learn AI in 2025
5. LLM and GenAI Frameworks (Hugging Face Transformers, LangChain)
The rise of LLM (Large Language Models) and GenAI frameworks is reshaping how professionals deploy AI solutions. While traditional and deep learning frameworks remain the foundation, these cutting-edge tools are enabling the development of smarter, production-grade AI systems.
Career Relevance
If you're aiming to thrive as an ML Engineer, AI Scientist, or Backend ML Developer by 2026, mastering frameworks like Hugging Face Transformers and LangChain is essential. Hugging Face gives you access to over a million pre-trained models, such as GPT, BERT, and Llama, which can be fine-tuned and deployed for tasks like NLP and multimodal applications. On the other hand, LangChain acts as the glue that connects these LLMs to private data, APIs, and memory systems within an organization.
A key skill employers are seeking is the ability to build Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) workflows. These workflows are becoming the go-to architecture for enterprise AI, powering tools like internal "copilots", generative dashboards, and intelligent chatbots. Whether you're in fintech, legal tech, or AI-driven journalism, these frameworks help you move beyond theory to creating real-world products - an ability highly valued by employers today.
Industry Demand
The job market is increasingly favoring professionals who can not only deploy AI models but also monitor and scale them effectively. Hugging Face is widely used for customer-facing applications like chatbots and document processing, while LangChain integrates LLMs with vector databases, CRMs, and other systems through a vast library of over 600 integrations.
"The future of machine learning is production-ready, collaborative, and LLM-aware. In 2026, successful ML professionals won't just build models - they'll ship and scale them, responsibly." – Machine Learning Jobs
Startups creating AI productivity tools and enterprises modernizing their workflows are leading the demand for these skills. Employers want candidates who understand the entire process - from data ingestion using LangChain to fine-tuning models on Hugging Face - and can showcase their expertise through public GitHub projects or similar portfolios using free job application tools.
Learning Curve
Both Hugging Face and LangChain are accessible for those with a solid grasp of Python. Hugging Face’s model hub makes it easy to experiment with pre-trained models, although mastering techniques like tokenization and fine-tuning requires dedicated effort. LangChain, known for its developer-friendly interface, allows rapid prototyping, but building functional RAG applications will require familiarity with vector embeddings and databases like Pinecone or Qdrant.
The real hurdle isn’t the frameworks themselves - it’s acquiring the complementary skills to make your work production-ready. This includes understanding prompt engineering, integrating APIs like OpenAI or Anthropic, and applying model compression techniques with tools like ONNX. While the learning curve is moderate, the skills you gain can be applied to real-world projects in a matter of weeks. Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can start incorporating specialized tools to tackle complex, production-level challenges.
Complementary Skills/Tools
To excel in LLM and GenAI workflows, focus on the following:
- Vector databases like Pinecone and Qdrant for semantic search and data retrieval.
- LangGraph for creating multi-step agent systems and orchestrating complex workflows.
- API integration with platforms like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Cohere for deploying AI solutions.
As responsible AI practices become a priority, tools like SHAP and LIME for explainability, along with bias detection frameworks like Fairlearn, can set you apart. Employers value professionals who can demonstrate end-to-end fluency - from data ingestion and model development to CI/CD pipelines and monitoring tools like Grafana. By showcasing projects that include dashboards and fully operational pipelines, you’ll prove your ability to deliver scalable, production-ready AI systems. To streamline your search for these high-stakes roles, consider using human assistants to manage your applications.
Framework Comparison
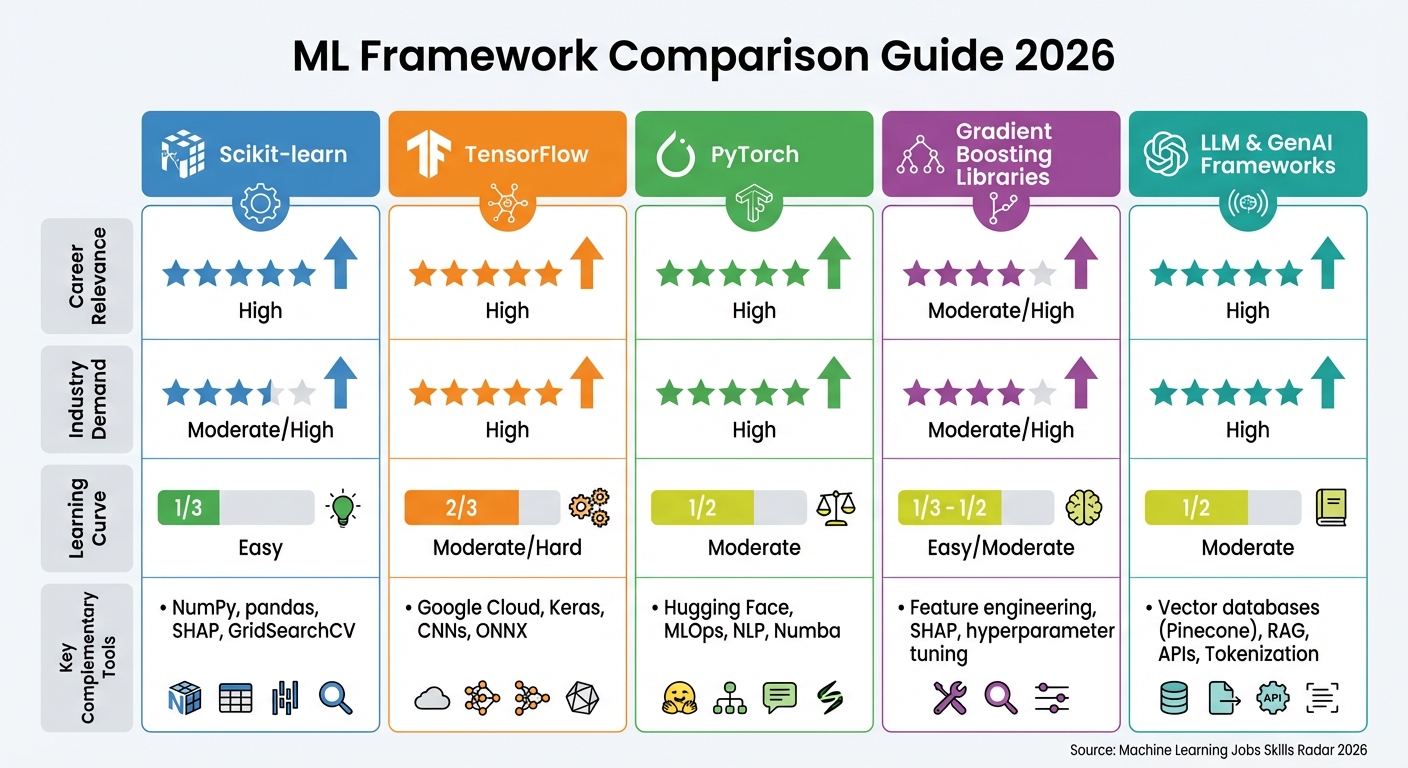
Top ML Frameworks Comparison: Career Relevance, Industry Demand, and Learning Curve for 2026
Selecting the best machine learning framework depends heavily on your career goals and the industry you're targeting. The table below breaks down how various frameworks align with key factors that employers value most in 2026.
| Framework | Career Relevance | Industry Demand | Learning Curve | Complementary Skills/Tools |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scikit-learn | High | Moderate/High | Easy | NumPy, pandas, SHAP, GridSearchCV |
| TensorFlow | High | High | Moderate/Hard | Google Cloud, Keras, CNNs, ONNX |
| PyTorch | High | High | Moderate | Hugging Face, MLOps, NLP, Numba |
| Gradient Boosting Libraries | Moderate/High | Moderate/High | Easy/Moderate | Feature engineering, SHAP, hyperparameter tuning |
| LLM and GenAI Frameworks | High | High | Moderate | Vector databases (Pinecone), RAG, APIs, Tokenization |
This table provides a snapshot of each framework's strengths, but let’s dive into what makes each one stand out.
Scikit-learn is the go-to framework for beginners, especially those looking to build a foundation in classical machine learning. It’s perfect for roles in small to mid-sized enterprises (SMEs), fintech, or data analysis. Its user-friendly design and extensive documentation make it an excellent starting point for anyone entering the field.
For deep learning roles, TensorFlow and PyTorch are the heavyweights. TensorFlow shines in large-scale production environments and supports seamless cross-platform deployment. On the other hand, PyTorch’s Python-friendly interface and integration with tools like Hugging Face make it a favorite for research-focused work and natural language processing (NLP) applications.
If your career path leads to finance, insurance, or risk modeling, you’ll want to master Gradient Boosting Libraries like XGBoost and LightGBM. These frameworks dominate when it comes to handling tabular data, making them the industry standard for tasks like pricing models and fraud detection.
For those eyeing roles in startups or cutting-edge AI products, LLM and GenAI frameworks are essential. These frameworks are at the heart of building retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) workflows and deploying chatbots that are ready for production. Familiarity with tools like vector databases (e.g., Pinecone) and tokenization techniques will give you an edge.
One thing is clear: employers in 2026 are looking for more than just model-building skills. They expect candidates to have experience with production-ready tools like MLflow, Docker, and monitoring systems such as Grafana. The ability to deploy and maintain robust systems is just as important as creating the models themselves. Using a virtual assistant for your job search can help you manage these complex requirements while applying for roles.
Conclusion
Choosing the right framework can shape your career trajectory in machine learning. If you're aiming for deep learning roles at major tech companies like Google or Amazon, TensorFlow is ideal for creating production-ready neural networks. For research-focused positions or NLP projects, PyTorch provides the flexibility necessary for experimentation and innovation. Meanwhile, entry-level data scientists and analysts will find Scikit-learn invaluable for traditional machine learning tasks. For roles centered on structured data, particularly in industries like finance or e-commerce, Gradient Boosting Libraries such as XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost are highly sought after.
With machine learning adoption growing by 250%, employers are prioritizing candidates who can deliver measurable, deployable results. In such a competitive market, showcasing expertise in these frameworks is crucial.
Here’s a sobering fact: 75% of resumes never make it to a human recruiter, and only 2% of applicants typically secure an interview. However, using AI-powered resume tools can increase your chances of a callback by up to 30%. This is where scale.jobs becomes a game-changer for U.S.-based machine learning professionals.
Scale.jobs scans over 2 million job postings to match your specific skills - whether it’s PyTorch for computer vision or XGBoost for structured data modeling. Their AI Assistant Pro plan, available at a launch price of $9/month, creates ATS-friendly resumes tailored to individual job descriptions, maximizing keyword visibility. For those needing extra support, the Human Assistant service employs trained reverse recruiters who handle your applications, provide proof-of-submission screenshots via WhatsApp, and save you 20+ hours a week.
Whether you’re a recent graduate stepping into data science, a professional transitioning into ML engineering after a career setback, or an H-1B visa holder navigating unique challenges, aligning your framework expertise with targeted opportunities can set you apart from the competition.
FAQs
What are the main differences between TensorFlow and PyTorch for deep learning jobs?
TensorFlow is built around static computation graphs, making it a solid choice for large-scale, production-ready applications. Its ecosystem is robust, featuring tools like TensorFlow Serving that simplify deployment in industrial environments.
Meanwhile, PyTorch stands out with its dynamic computation graphs, offering a more flexible and Pythonic approach. This flexibility makes it especially popular among researchers and developers who prioritize quick prototyping and easier debugging. In the end, the decision often comes down to whether your priority lies in research or scaling for production.
How can I use Scikit-learn to boost my job prospects in finance and healthcare?
To catch the attention of recruiters in finance and healthcare, consider using Scikit-learn to craft machine learning models tailored to these industries. In finance, classification algorithms like logistic regression or random forests can be employed to create systems for credit-risk assessment or fraud detection. For tasks like predicting stock prices, regression techniques such as gradient boosting are highly effective. On the healthcare side, similar methods can be utilized to build models for patient diagnosis or forecasting clinical outcomes.
Make your work stand out by sharing your code, results, and performance metrics on platforms like GitHub or your personal portfolio site. This not only highlights your technical skills but also shows how you can solve practical, high-stakes problems in industries that are always on the lookout for skilled professionals.
What additional skills should I learn to complement gradient boosting libraries and advance my ML career?
When working with tabular data, tools like XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost are some of the best in the game. But if you're looking to grow as a machine learning professional, there's more to the journey than just mastering these libraries. Building a diverse skill set can open up new opportunities and take your career to the next level.
Start with data preprocessing and feature engineering. These are the backbone of any successful model. Learn to clean messy datasets, handle missing values, and craft features that truly capture the essence of the data. These skills can make a world of difference in how well your models perform.
Next, dive into model evaluation and hyperparameter tuning. Techniques like cross-validation and early stopping not only improve your model's reliability but also help you fine-tune it to perform at its best. These are essential steps to ensure your results are both accurate and consistent.
To stand out in the field, it's also important to develop software engineering fundamentals. Get comfortable with Python, learn how to use version control systems like Git, and practice writing clean, modular code that others can easily understand and reuse. Employers value these skills just as much as your knowledge of algorithms.
On top of that, gaining experience with MLOps and deployment tools can set you apart. Tools like Docker and cloud platforms such as AWS or GCP can help you deploy machine learning models into production and monitor them effectively. This ability to take a project from development to deployment is increasingly sought after in the industry.
Finally, don't underestimate the importance of a solid grounding in statistics and probability. These fundamentals will not only help you interpret your results but also allow you to explain your findings clearly to others, whether they're technical peers or non-technical stakeholders.
By mastering these areas, you'll position yourself as a well-rounded machine learning professional capable of delivering comprehensive, end-to-end solutions.




