Python for Data Analysis: Career Benefits
Mastering Python reshapes data-analysis careers with higher pay, broader job options, and the skills needed for AI and machine learning roles.

Python is the most sought-after skill for data analysis jobs in 2026. Here's why:
- High demand: Data scientist roles are growing 34% from 2024 to 2034, and 65% of job postings now require Python.
- Higher salaries: Python-trained professionals in the U.S. earn $103,694 on average, compared to $70,811 for non-Python analysts.
- Replacing outdated tools: While 70% of companies still use Excel, Python handles massive datasets, automates tasks, and reduces errors.
- Future-proof: Python is essential for AI and machine learning, with 1.4 million new data-focused jobs expected by 2027.
Want to stay competitive in the job market? Master Python, build a portfolio with tools like Pandas, NumPy, and Scikit-learn, and highlight your skills with an AI resume builder. Python isn't just a skill - it's a career game-changer.
The Problem: More Jobs Than Qualified Python Analysts
Job Market Numbers and Salary Data
The demand for Python-skilled data scientists is outpacing the available talent pool. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, there will be approximately 23,400 new job openings for data scientists every year through 2034. These aren't just existing roles being refilled - they're brand-new positions. Yet, companies are finding it increasingly difficult to hire because there simply aren’t enough qualified candidates.
Recent data highlights just how central Python has become in this field. Between July 2024 and June 2025, 65% of job postings for data scientists listed Python as a required skill. It’s no longer optional - it’s the standard. In fact, LinkedIn recognized both "Python" and "Data Analysis" among the top 10 most in-demand hard skills globally in 2023. Despite this, the talent pool isn’t growing fast enough to meet the need.
The salary figures tell a similar story. As of early 2026, data scientists proficient in Python earn an average of $103,694 annually, with the top 10% earning over $143,000. In comparison, general data analysts without Python skills earn around $70,811 - a difference of nearly $33,000 per year. The World Economic Forum also forecasts 1.4 million new data-focused jobs by 2027, further widening the gap between demand and supply.
Why Candidates Without Python Skills Fall Behind
Traditional tools like Excel are no longer sufficient for modern data analysis. Python addresses these shortcomings, enabling users to process massive datasets and automate time-consuming tasks. Employers now expect candidates to bring these capabilities to the table.
When job postings require Python, they’re looking for more than just basic data analysis. They want professionals who can deliver automation, scalability, and reproducibility. As Michael Berthold, CEO of KNIME, points out:
"Most new tools in the artificial intelligence/machine learning space have been developed in Python, so you need to know Python in order to work directly with those libraries."
Without Python skills, candidates are effectively shut out of the fastest-growing areas of the job market, including AI and machine learning. These fields are reshaping the way companies approach data, making Python proficiency a non-negotiable skill.
The job market is evolving rapidly, and the expectations for candidates are rising just as quickly. For instance, 5% of job postings in 2023 required natural language processing (NLP) expertise. By 2024, that number had jumped to 19%. Employers increasingly want "full-stack" data professionals - those who can handle everything from data engineering to visualization, all built on Python. Laura Baldwin, President of O'Reilly, emphasizes the urgency:
"Given the shortage of qualified employees in fields like data science, machine learning, and AI, companies that are serious about building out their workforces must invest in learning and training to grow this talent internally."
Is Python Really Needed For a Data Analyst Job?
Why Python Works: A Practical Tool for Data Analysis
Python addresses the key challenges that traditional data analysis methods often face. While many companies - around 70% - still depend on spreadsheets, studies reveal that 94% of business spreadsheets contain errors. Python sidesteps this issue by offering code-based workflows that are transparent, testable, and reproducible. With Python scripts, you get consistent results every time, eliminating the manual errors that spreadsheets are prone to.
One of Python's biggest strengths is its simplicity and efficiency. It's a high-level, interpreted language that reads almost like regular English, making it beginner-friendly even for those with no prior coding experience. Plus, Python's ability to handle massive datasets far surpasses tools like Excel, which caps out at about 1 million rows. Python can process millions - or even billions - of records without breaking a sweat. This scalability has made it the go-to tool for over 90% of data science professionals, compared to 53% for SQL and 38% for R.
Main Python Libraries for Data Work
Python's versatility comes from its specialized libraries, each tailored for specific tasks in data analysis:
- Pandas: Perfect for data manipulation, offering DataFrame structures to clean and organize data.
- NumPy: The backbone of numerical computing, providing fast and efficient arrays.
- Matplotlib: A go-to library for creating detailed and customizable charts.
- Seaborn: Built on Matplotlib, it simplifies the creation of visually appealing statistical graphics with polished default settings.
- Scikit-learn: A powerful tool for machine learning tasks like classification, regression, and clustering.
These five libraries - Pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, Seaborn, and Scikit-learn - are essential for modern data work and appear in 78% of data scientist job postings as of 2023. Together, they allow analysts to transform raw data into meaningful insights.
How Companies Use Python for Data Analysis
Businesses rely on Python to streamline repetitive tasks that traditionally consume analysts' time. Instead of manually transferring data between spreadsheets or adjusting formulas across multiple files, Python scripts automate these workflows. This not only reduces errors but also saves hours of work each week. To maximize your efficiency further, you can land jobs faster with the help of human assistants who handle the application process for you. For example, in healthcare, analysts use Python to pull pharmacy data from various sources, standardize reports, and identify anomalies - tasks that would take days to complete manually.
Python also enables advanced analytics that shape critical business decisions. Companies use it for statistical modeling, forecasting trends, and implementing machine learning - capabilities that go far beyond what Excel can handle. Notably, 65% of highly data-driven small businesses outperform their competitors, compared to just 33% of less data-focused counterparts. Michael Berthold, CEO of KNIME, highlights Python's importance:
"Most new tools in the artificial intelligence/machine learning space have been developed in Python, so you need to know Python in order to work directly with those libraries."
Career Benefits of Learning Python for Data Analysis
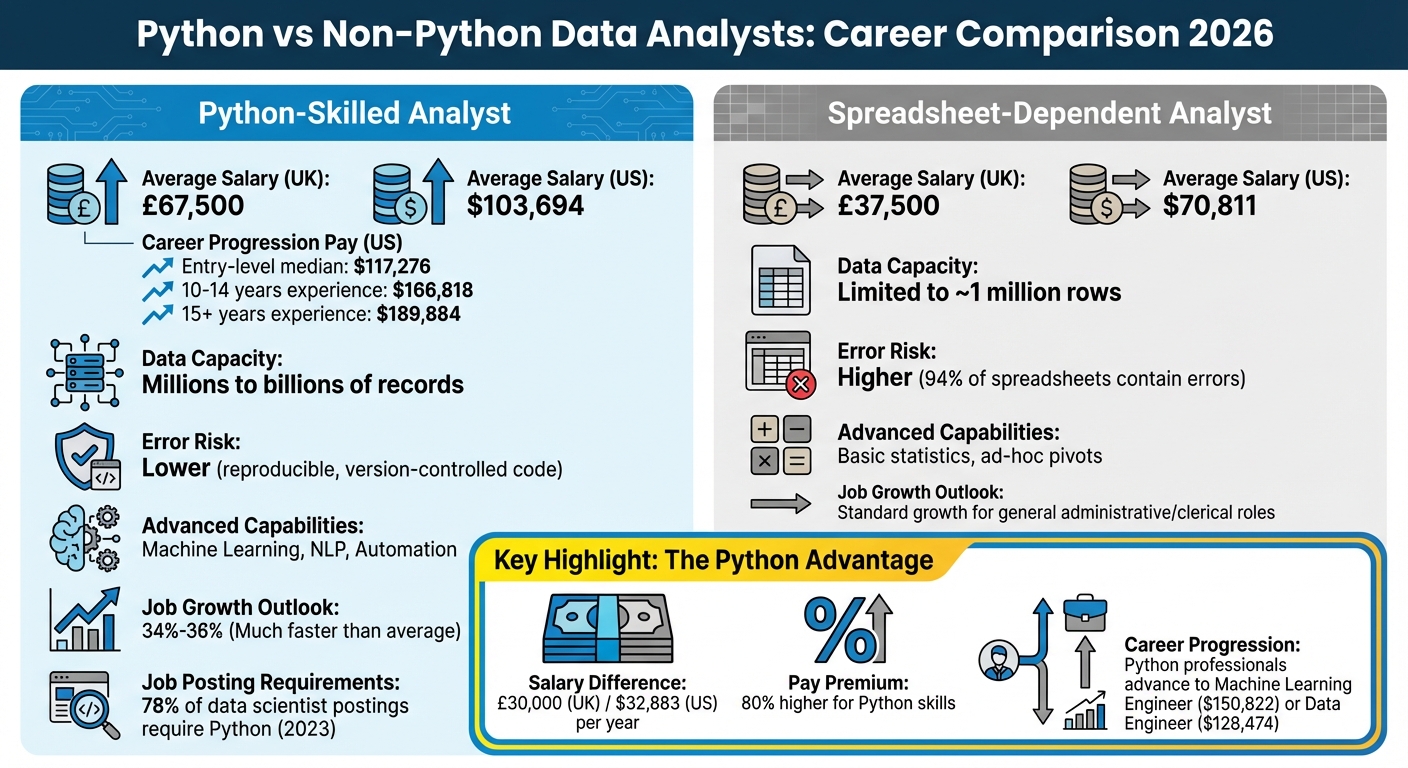
Python vs Non-Python Data Analysts: Salary and Career Comparison 2026
Higher Pay for Python-Skilled Professionals
If you're skilled in Python, the financial rewards can be substantial. In the UK, professionals with Python expertise earn an average of £67,500 annually, compared to just £37,500 for those who rely solely on Excel - a striking 80% pay premium. In the U.S., the numbers are equally compelling. As of January 2026, the average salary for a Data Scientist with Python skills is $103,694, with the median reaching $112,590 by May 2024.
Even at the entry level, Python-trained data scientists earn a median of $117,276, far surpassing the $70,811 typical for non-Python analysts. The financial benefits only grow with experience. Professionals with 10-14 years in the field see their median pay rise to $166,818, while those with 15+ years can earn $189,884 or more annually.
Why does Python command such high salaries? Its ability to handle massive datasets and support advanced tasks like machine learning makes it indispensable. These skills qualify you for high-paying roles such as "Data Scientist" or "Machine Learning Engineer", which offer significantly better compensation than general "Data Analyst" positions. Python's central role in artificial intelligence and machine learning makes it one of the most sought-after skills in the job market.
And it's not just about the paycheck. Python expertise also opens up a variety of career paths across industries, giving you the flexibility to shape your professional future.
More Job Options Across Industries
Python skills give you the freedom to explore careers in multiple fields rather than confining you to a single path. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, data scientist roles are expected to grow by 34% to 36% from 2024 to 2034 - far outpacing the average growth rate for most occupations. This surge in demand highlights the increasing need for Python expertise across industries.
While Technology & Engineering leads the way, accounting for 28.2% of Python-related data roles, other sectors are catching up. Health & Life Sciences claims 13%, and Financial & Professional Services represent 10% of the demand. Python's versatility means you can branch into roles like marketing analyst, financial analyst, product manager, or even full-stack data engineer.
The job market also favors Python-trained professionals during economic shifts. In 2023, data scientists made up only 3% of tech layoffs, compared to 22% for software engineers. With demand for AI and machine learning specialists projected to rise by 40% by 2027, Python proficiency not only increases your job prospects but also provides stability in an ever-changing market. To accelerate your transition into these high-growth roles, you can land jobs faster with human assistants who handle the application process for you.
Python vs. Non-Python Data Analysts: A Comparison
The differences between Python-trained professionals and those who rely on spreadsheets go far beyond salary. Python users tackle tasks that Excel simply can't handle, from processing massive datasets to automating workflows and applying machine learning techniques. These advanced capabilities make Python a game-changer in the data world.
| Feature | Python-Skilled Analyst | Spreadsheet-Dependent Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Average Salary (UK) | £67,500 | £37,500 |
| Data Capacity | Millions to billions of records | Limited to ~1 million rows |
| Error Risk | Lower (reproducible, version-controlled code) | Higher (94% of spreadsheets contain errors) |
| Advanced Capabilities | Machine Learning, NLP, Automation | Basic statistics, ad-hoc pivots |
| Job Growth Outlook | 34%–36% (Much faster than average) | Standard growth for general administrative/clerical roles |
Career trajectories also differ significantly. Python-trained professionals often move into specialized, high-paying roles like Machine Learning Engineer (average salary: $150,822) or Data Engineer ($128,474). In contrast, spreadsheet-dependent analysts are more likely to plateau in lower-paying positions. In 2023, 78% of data scientist job postings specifically required Python skills, signaling that employers now view Python proficiency as a must-have for competitive roles in data analysis.
These comparisons make one thing clear: mastering Python not only boosts your earning potential but also sets you on a fast track to career advancement. Whether you're aiming for higher pay, job security, or more opportunities, Python is the tool to help you achieve your goals.
How to Start Learning Python for Data Analysis
Start with Python Basics and Core Libraries
Before diving into data analysis, make sure you’ve got a solid grasp of Python fundamentals. This means understanding the basics like syntax, control structures, and functions. Once you've nailed these, it’s time to explore the core libraries that make Python such a powerhouse for data analysis: pandas for manipulating and cleaning data, NumPy for handling numerical computations, and Matplotlib for creating visualizations.
After gaining confidence with these essential tools, expand your toolkit with libraries like Seaborn for creating more visually appealing charts and Scikit-learn for implementing machine learning algorithms. These libraries are frequently mentioned in job descriptions and are key to many data analysis roles. To learn them, you can use free resources like YouTube or platforms like DataCamp. If you're open to paid options, sites like Udemy and 365 Data Science offer project-based courses that simulate real-world scenarios.
The key is to focus on the skills that are most in demand rather than trying to learn everything at once. With a strong foundation, you’ll be ready to start building projects that showcase your abilities.
Build Projects to Demonstrate Your Expertise
Once you’ve got the basics down, it’s time to show what you can do by working on real-world projects. Employers want to see that you can handle actual datasets - not just theoretical exercises. Aim to complete three to five projects that highlight your ability to import, clean, analyze, and visualize data. Use Jupyter Notebooks to document your process; they’re widely used in the industry for combining code, visuals, and explanations in a single, shareable file.
Choose projects that tackle real problems. For instance, you could analyze Netflix trends to uncover patterns in genres and movie durations, examine NYC public school SAT scores to find the best-performing boroughs, or map crime data in Los Angeles to identify high-risk times and locations. These types of projects show that you can work with messy, unstructured data and turn it into meaningful insights.
Once your projects are complete, host them on GitHub to create a portfolio that recruiters can easily access. You can also use tools like Streamlit to turn your Python scripts into interactive web applications, demonstrating your ability to create tools that stakeholders can actually use. For an extra challenge, consider joining Kaggle competitions. They’re a great way to test your skills against others and build professional credibility.
With your portfolio ready, you’ll be well-positioned to start applying for jobs.
Leverage Job Search Tools to Land a Role
After building a strong portfolio, it’s time to turn your Python skills into job offers. Job hunting can be time-consuming - manual searches can take 20+ hours a week - so using the right tools can save you a lot of effort.
Why scale.jobs is a standout choice for Python-trained analysts
While platforms like Jobscan focus on optimizing resumes for applicant tracking systems (ATS), scale.jobs goes further by offering human-powered application services. Here’s why it’s a great fit for data analysts with Python expertise:
- Human-submitted applications: Unlike auto-apply tools like LazyApply, scale.jobs uses trained virtual assistants to manually submit your applications, reducing the risk of being flagged by ATS systems.
- Python-specific resume tailoring: Their AI creates resumes tailored to highlight your experience with tools like pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib for specific job postings - something generic resume builders can’t match.
- Transparent pricing: Instead of monthly subscriptions, you pay a flat fee for 250, 500, or 1,000 applications (starting at $199). Unused credits are refunded.
- Real-time updates: You get WhatsApp notifications and screenshots showing when and where your applications were submitted - offering a level of accountability that many platforms lack.
- Fast turnaround: Custom resumes and cover letters are ready within 24 hours, saving you from the time-consuming process of creating them yourself.
The free tier includes tools like an ATS-compliant resume builder and job application tracker. For $9/month, the AI Assistant Pro plan offers unlimited tailored resumes and cover letters, which is especially useful when applying to multiple roles that emphasize different Python skills. The Human Assistant service, starting at $199, handles everything from resume customization to application submissions, freeing up your time for networking and interview prep.
Additional features include a Resume ATS Checker to ensure your Python projects and skills pass automated filters, a Salary Predictor to help you negotiate offers, and an Interview Questions Predictor to prepare for coding challenges on platforms like Leetcode or HackerRank.
A word of caution about auto-apply bots
Tools like LazyApply might seem convenient, but they often trigger red flags in modern ATS systems, leading to automatic rejections. With its human-powered approach, scale.jobs ensures your applications maintain the authenticity recruiters expect while saving you hours of manual effort.
Conclusion: How Python Can Change Your Career Path
Learning Python for data analysis can be a game-changer for your career. By mastering Python, you gain access to high-demand roles with competitive salaries, bridging the gap that often prevents skilled professionals from landing top-tier positions.
Python's versatility opens up opportunities across industries like finance, healthcare, marketing, and beyond. It's not just about becoming a "Data Scientist" - it's about equipping yourself for the rapid changes shaping the future of work. As Michael Berthold, CEO of KNIME, pointed out, Python is at the core of most new AI and machine learning tools, making it a must-have skill for anyone looking to work with cutting-edge technology.
To make the most of these opportunities, start by learning Python basics, build a strong portfolio and use an AI resume builder, and use targeted job search platforms to find the right role. Pair that with hands-on experience using data analysis tools, and you'll be well-prepared to apply your skills effectively. Python doesn't just keep you relevant - it places you at the forefront of AI-driven innovation. The real question is: how soon will you take the first step?
FAQs
What’s the best way to start learning Python for data analysis?
The most effective way to dive into Python for data analysis is by following a structured, hands-on approach that gradually develops your skills. Start with beginner-friendly courses on platforms like DataCamp or Coursera. These platforms are designed for those with little to no coding background and cover key topics such as Python basics, working with data using pandas, performing numerical operations with NumPy, and creating visualizations with Matplotlib and Seaborn.
After mastering the fundamentals, it's crucial to practice with real-world datasets. This helps you gain experience in cleaning, analyzing, and visualizing data - tasks you'll often encounter in a professional setting. To stand out to potential employers, consider completing a portfolio project that demonstrates an end-to-end analysis. This not only highlights your technical skills but also shows your ability to manage a project from start to finish.
Lastly, tools like scale.jobs can assist in crafting ATS-friendly resumes and tailored applications, giving you an advantage when applying for data analysis roles.
What are the key Python libraries for data analysis?
When it comes to Python libraries for data analysis, a few stand out as must-haves. Pandas is perfect for handling and manipulating data, while NumPy excels at numerical computations. For visualizing your data, Matplotlib and Seaborn are go-to options.
If machine learning or statistical modeling is part of your workflow, you’ll find Scikit-learn, Statsmodels, and SciPy to be incredibly useful. And for those looking to add interactivity to their visualizations, Plotly is a fantastic choice.
These libraries are staples in the data analysis world, offering tools that can elevate your ability to process and present data - skills that are essential for anyone aiming to build a career in this field.
How can learning Python for data analysis boost my career in data science?
Python has become an essential skill for anyone looking to thrive in data science, thanks to its growing demand and versatility. In 2023, it was featured in a whopping 78% of job postings, and all signs point to it remaining one of the most sought-after skills in 2024. Its appeal lies in its robust libraries, ease of use, and a highly active user community, making it an indispensable tool for tackling complex data challenges with efficiency.
Learning Python doesn’t just boost your chances of landing a job - it can also significantly increase your earning potential. Data scientists skilled in Python earn an average salary ranging from $103,000 to $108,000 per year in the United States. Whether you're just embarking on your career or aiming to level up, Python can help you stand out in a competitive job market.




