5 Best Practices for Candidate Data Security in ATS
Secure candidate data in your ATS with AES-256/TLS, RBAC + MFA, timely patches, encrypted backups, and staff training to meet GDPR/CCPA and cut breach risk.

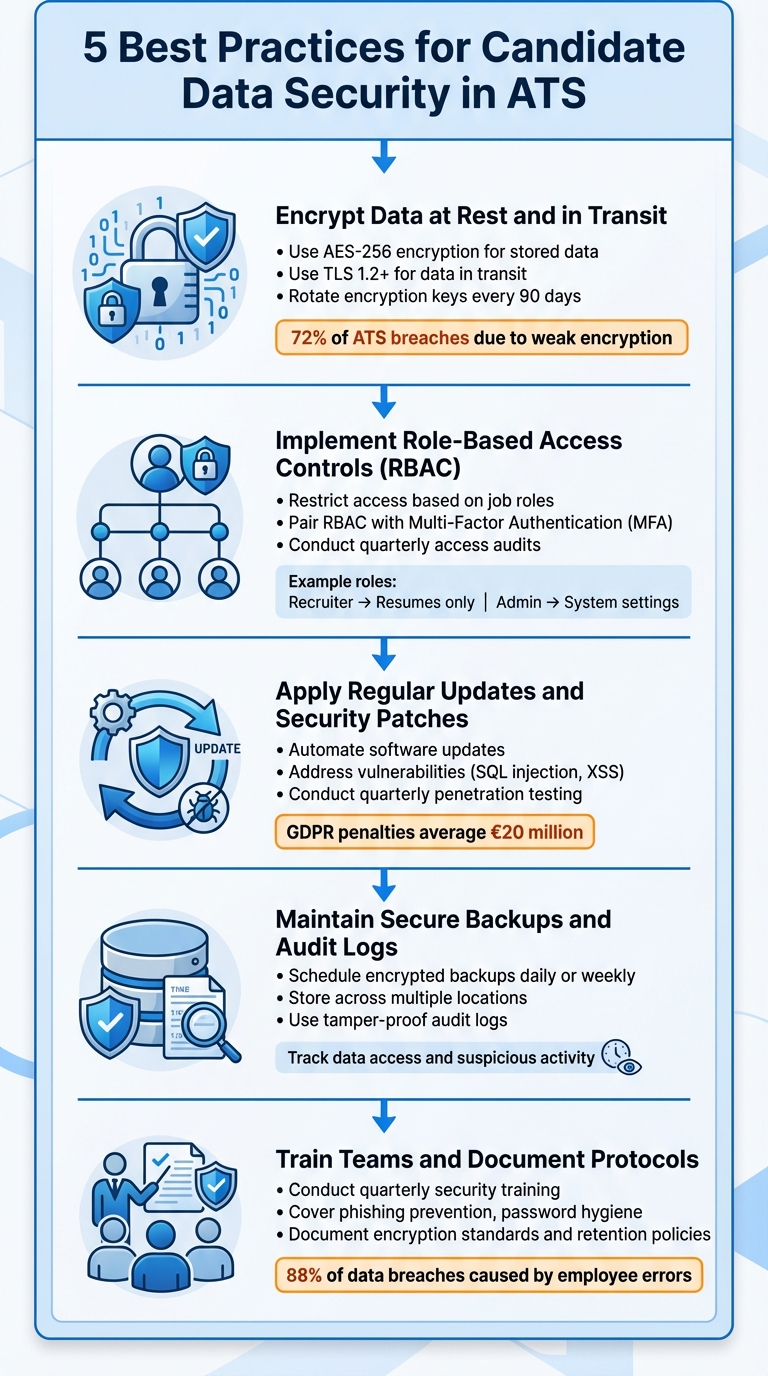
Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) store sensitive candidate information, making them attractive targets for cyberattacks. To ensure data security, organizations must adopt robust measures that comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA while fostering trust with candidates. Below are five practical strategies to secure candidate data effectively:
- Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit: Use AES-256 encryption for stored data and TLS 1.2+ for data in transit. Regularly rotate encryption keys (every 90 days) to minimize risks. Secure document exchange methods like SFTP or OAuth-based APIs add an extra layer of protection.
- Implement Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC): Restrict data access based on job roles. For example, recruiters can access resumes, while administrators manage system settings. Pair RBAC with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and conduct quarterly access audits.
- Apply Regular Updates and Security Patches: Automate software updates to address vulnerabilities like SQL injection or XSS. Regular penetration testing and vulnerability scans ensure your ATS remains secure against emerging threats.
- Maintain Secure Backups and Audit Logs: Schedule encrypted backups daily or weekly and store them across multiple locations. Use tamper-proof audit logs to track data access and suspicious activity, ensuring compliance with data protection laws.
- Train Teams and Document Protocols: Conduct quarterly security training on phishing prevention, password hygiene, and breach response. Document encryption standards, retention policies, and incident response steps for clarity and consistency.
These measures not only protect sensitive information but also reduce the risk of breaches caused by employee errors, which account for 88% of data breaches. For organizations managing high application volumes, using a job application service or virtual assistant for job seekers can streamline processes while maintaining data security.
Quick Comparison of ATS Security Features
| Feature | Encryption | Access Control | Compliance Certifications | Data Retention |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scale.jobs | AES-256, TLS 1.2+ | RBAC + MFA | GDPR, CCPA, DPF | Purpose-based retention |
| CVViZ | End-to-end encryption | RBAC + MFA | SOC 2, ISO 27001 | Automated deletion policies |
| Hireology | SSL (TLS 1.2) | Strong passwords | Local privacy laws | Documented privacy policy |
| MokaHR | Automated key rotation | RBAC + MFA | GDPR, CCPA | Automated retention policies |
5 Best Practices for ATS Candidate Data Security
Data at Rest Encryption Going Beyond the Basics to Address Modern Attacks - Chuck Willis & Wias Issa
1. Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit
Encryption acts as a shield, protecting candidate data from unauthorized access. To secure data at rest, implement AES-256 encryption - this ensures sensitive details like resumes, Social Security numbers, and employment histories remain unreadable without the proper decryption key. For data in transit, rely on TLS 1.2 or higher to safeguard information as it moves across networks.
The stakes are high: even a small breach can compromise thousands of records. Consider this: in 2025, a multinational retail giant handling 2 million job applications relied on MokaHR's enterprise-grade encryption and CCPA compliance tools to maintain 100% security compliance, avoiding any breaches. Similarly, a Fortune 500 bank in the U.S. managed over 1 million resumes using Workday's encrypted ATS with a zero-trust architecture. The result? A 40% reduction in breach risks and a 25% cut in annual compliance costs.
To further minimize risks, robust key management is essential. Automated key rotation every 90 days can significantly reduce the impact of compromised credentials. It's worth noting that weak encryption is responsible for 72% of ATS breaches, making routine updates a necessity. If your organization handles high-volume hiring, ensure your ATS provider holds certifications like SOC 2 Type II or ISO 27001, which confirm strong encryption standards.
Encryption is only part of the equation. Pair it with secure transfer protocols and additional layers of protection. Use secure document exchange methods such as SFTP or OAuth-based APIs and enforce multifactor authentication (MFA) alongside role-based access control (RBAC). These measures ensure that decrypted data is accessible only to authorized personnel. For example, in late 2024, a global manufacturer using Oracle ATS's AI compliance monitoring and SOC 2 logs reduced supply chain vulnerabilities by 25%, saving $1 million in potential audit fees.
2. Use Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC)
Expanding on encryption practices, implementing Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) ensures employees only access the candidate data necessary for their specific tasks - no more, no less. This method significantly reduces the chances of internal data exposure by restricting sensitive details, such as Social Security numbers or financial information, to a select group of authorized personnel. For instance, recruiters might only access resumes and contact details, while administrators oversee system configurations and audit logs. By assigning granular permissions - like "viewer", "editor", or "administrator" - you can customize access at the module level, reducing risks of data misuse.
RBAC enforces the "need-to-know" principle, offering an added layer of security when paired with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). For example, a hiring manager might only view candidates within their department, while a Data Protection Officer (DPO) monitors audit trails and consent logs without accessing recruitment data. This layered approach minimizes vulnerabilities tied to compromised credentials.
Regular audits are crucial for maintaining RBAC effectiveness. Conduct quarterly reviews of user accounts to ensure permissions align with current roles, and swiftly revoke access for employees who leave or transition to new positions. As MokaHR points out, "The results of assessments should be used to capture residual risks and inform security improvements." Automated tools can further enhance security by tracking login attempts, monitoring data access patterns, and flagging unusual activity before it becomes a problem.
| Role Type | Typical Permissions | Data Access Level |
|---|---|---|
| Administrator | Full system configuration, user management, audit log access | Full access to all candidate and system data |
| Recruiter | Create job postings, move candidates through stages, add notes | Professional data (resumes, work history, contact info) |
| Hiring Manager | View assigned candidates, submit interview feedback | Limited to specific departments or job requisitions |
| Viewer | Read-only access to specific modules | No ability to edit or delete information |
When combined with strong encryption, RBAC strengthens your ATS by ensuring sensitive data is only accessible to those who need it. This is particularly vital for organizations scaling their hiring operations or handling sensitive visa documentation for international candidates. For added security and efficiency, consider using professional resume writing services that specialize in ATS compliance and data protection. Such services help candidates submit properly formatted, ATS-ready documents, reducing the need for manual handling and minimizing exposure of sensitive information during the hiring process.
While encryption safeguards data during storage and transfer, RBAC ensures only the right individuals access it. Together, these measures create a solid foundation for ongoing security enhancements in your ATS.
3. Apply Regular Software Updates and Security Patches
Keeping software up-to-date is one of the most effective ways to protect candidate data from cyberattacks. Software vulnerabilities, like SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS), are commonly exploited by hackers, and security patches are designed to fix these weak points. By applying updates promptly, you can close these gaps before attackers have a chance to exploit them. Automating this process ensures no update is overlooked, providing consistent protection against potential threats.
Automating updates minimizes the risk of human error and ensures your system stays prepared against emerging security challenges. Whenever a patch becomes available, implement it immediately to block known vulnerabilities. Enable automatic patching whenever possible, and make it a priority to conduct security assessments - such as penetration testing and vulnerability scans - on a quarterly basis. These measures not only enhance your defenses but also demonstrate your commitment to compliance with strict data protection regulations like GDPR, which imposes penalties averaging €20 million for violations, and the upcoming NIS2 standards set to raise the bar for security in 2026.
"Data security is a continuous event that requires vigilance, regular updates, and constant improvement." – Vybog
Additionally, adopt strong key management practices, such as rotating encryption keys every 90 days using AI-driven tools. As mentioned earlier, robust key management significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. AI can also assist by auto-classifying personally identifiable information (PII), redacting sensitive data, and identifying compliance gaps before audits. When selecting an applicant tracking system (ATS) provider, confirm they hold SOC 2 Type II and ISO 27001 certifications - self-attested or lower-level certifications like Type I may no longer meet auditors' expectations.
| Security Activity | Frequency | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Software Patching | Immediate / Automated | Closes known vulnerabilities to prevent attacks |
| Encryption Key Rotation | Every 90 Days | Limits exposure if a key is compromised |
| Security Audits | Quarterly or Biannually | Detects hidden vulnerabilities and risks |
| Data Backups | Daily or Weekly | Ensures quick recovery after breaches or failures |
4. Keep Secure Backups and Audit Logs
In addition to encryption and access control, maintaining secure backups and detailed audit logs is essential for safeguarding your ATS (Applicant Tracking System). Encrypted backups and comprehensive audit logs act as crucial defenses against data loss and unauthorized access. To ensure no candidate records are lost, schedule backups daily or weekly, employing end-to-end encryption with AES-256 standards. Store these backups across multiple locations - using a combination of secure local servers and trusted cloud storage. This way, even if a ransomware attack or hardware failure occurs, your database remains intact. Quarterly simulation tests are a must to confirm that your backups are functional and your restoration process is seamless when needed. This approach complements the security measures already in place for your ATS.
Audit logs serve as a detailed record of all interactions with candidate data, including user logins, document views, edits, deletions, timestamps, and IP addresses. Such logs are critical for regulatory audits and breach investigations, as they provide a clear trail of who accessed what and when. To stay ahead of potential threats, implement real-time alerts for unusual activities like repeated login failures or bulk data downloads. Given that 88% of data breaches are linked to employee errors, tamper-proof audit logs not only ensure accountability but also provide opportunities for employee training to prevent future mistakes.
To further protect your backups and logs, implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), limiting access to only those administrators who need it. Strengthen security by requiring Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all entry points and regularly rotating encryption keys used for backups. These measures significantly reduce vulnerabilities. You might also consider partnering with professional resume and career services that follow enterprise-level security protocols, allowing you to focus on hiring while keeping candidate data secure.
Automating your backup schedule within the ATS minimizes human error, while automated retention policies ensure outdated candidate records are deleted in compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Modern ATS platforms can even generate compliance reports in under five minutes, simplifying regulatory reviews and helping you avoid penalties, which can average $20 million for major violations.
5. Train Teams and Document Security Protocols
Even the most secure ATS can fall short if the team using it isn't properly trained. Regular training and clear, actionable protocols are essential to ensure everyone understands their role in maintaining data security. Employees need to recognize phishing attempts, avoid accessing the ATS on unsecured networks like public Wi-Fi, and know the exact steps to take if they suspect a breach. A strong security framework combines advanced technology with a well-informed team.
Plan security training sessions every quarter or at least twice a year to address new and emerging threats. These sessions should cover key topics such as identifying phishing emails, creating strong passwords, using multi-factor authentication (MFA), and handling sensitive data correctly. To make the training more practical, conduct simulations like phishing drills or mock breach scenarios. For example, employees can practice spotting suspicious credential requests or identifying unusual sender email addresses. Mock breach exercises also allow teams to rehearse incident response plans, so they are prepared to act swiftly and effectively during an actual security event.
All security protocols should be documented in plain, straightforward language. Include essential details like encryption standards (e.g., SSL/TLS for data in transit and AES-256 for data storage), Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) definitions, patch management schedules, and requirements for audit logs. Clearly outline your data retention policies, specifying how long candidate data is stored and the secure methods for deletion, such as data wiping or physical shredding. Your breach response plan should also be included, with step-by-step guidance for containment, investigation, and transparent communication with affected candidates and regulatory agencies.
Incorporating compliance training into your security program reinforces best practices. Employees should understand regulations like GDPR’s right to be forgotten, CCPA’s opt-out rules, or industry-specific standards such as HIPAA. If your organization processes a high volume of candidate data, appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) can help oversee compliance and address risks that automated systems may not detect. For remote ATS access, enforce the use of VPNs and MFA to reduce vulnerabilities.
When working with professional career services or third-party vendors involved in handling candidate applications, ensure they adhere to enterprise-grade security standards. Look for certifications like SOC 2 or ISO 27001 to confirm their compliance. Conduct regular audits to monitor data access, revoke permissions as employee roles change, and automate data retention policies to securely delete outdated records in accordance with regulations. These steps create a well-rounded approach to safeguarding sensitive information.
ATS Security Features Comparison
When evaluating ATS platforms, understanding how they secure candidate data is critical. Security measures like encryption standards, access controls, and compliance certifications vary widely, shaping how well these systems protect sensitive information. For instance, Hireology enforces SSL (TLS 1.2) for all communications, whereas CVViZ employs end-to-end encryption for both stored and transmitted data. Meanwhile, MokaHR takes it a step further with automated key rotation, reducing the risk of long-term data breaches.
Access controls are another key focus area. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), which limits data visibility to employees based on their job roles, has become a standard. CVViZ and MokaHR enhance RBAC with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), adding another layer of protection against unauthorized access. Top Echelon, on the other hand, offers highly customizable RBAC permissions, allowing administrators to define roles like "viewer" or "editor" and restrict access to specific modules.
Compliance certifications further demonstrate a platform's commitment to security. CVViZ holds SOC 2 and ISO 27001 certifications, which involve independent audits of their security protocols. Scale.jobs, meanwhile, adheres to international frameworks like the EU-U.S. Data Privacy Framework (DPF), the UK Extension, and the Swiss-U.S. DPF. It also complies with GDPR for EEA/UK/Swiss residents and CCPA for California residents, ensuring that personal data is accessible only to those with a "legitimate business need." The following table provides a snapshot of how these platforms align with key security requirements:
| Feature | Scale.jobs | CVViZ | Hireology | MokaHR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Physical & technological measures | End-to-end encryption | SSL (TLS 1.2) | Automated key rotation |
| Access Controls | RBAC & legitimate business need | RBAC + MFA | Strong password enforcement | RBAC + MFA |
| Compliance | GDPR, CCPA, DPF | GDPR, CCPA, SOC 2, ISO 27001 | Local/federal privacy laws | GDPR, CCPA |
| Data Retention | Purpose-based retention | Automated deletion policies | Documented privacy policy | Automated retention policies |
The differences among these platforms often come down to the depth of certifications and encryption protocols. For example, CVViZ shines with its third-party audited certifications, while Scale.jobs prioritizes international data transfer frameworks.
For job seekers using platforms like Scale.jobs, the combination of automated security and human-assisted processes offers an extra layer of protection. Rather than relying solely on automated systems that may store credentials or require persistent API access, Scale.jobs employs trained virtual assistants to handle applications manually. This approach minimizes the risk of exposing sensitive data by limiting the digital attack surface.
If you're considering professional career services to manage your job applications, it's essential to ensure they maintain enterprise-grade security certifications and follow transparent data handling practices. These detailed comparisons can guide organizations and individuals in selecting platforms that prioritize both robust automated security and careful, human-assisted processes.
Conclusion
To safeguard your ATS effectively, focus on these critical measures: encryption protects data from being intercepted, role-based access controls limit unauthorized access, regular updates address potential vulnerabilities, secure backups provide a safety net against ransomware, and team training mitigates risks tied to human error - especially since 88% of data breaches are linked to employee mistakes. These steps build on the principles of encryption, access control, updates, backups, and training discussed earlier.
Security isn’t a one-and-done task. Cyber threats evolve constantly, and outdated software or untrained staff can create vulnerabilities. To stay ahead, conduct quarterly security audits, automate software updates, run phishing simulations, promptly revoke access for former employees, and test backup systems regularly.
For companies managing high volumes of applications, maintaining these security protocols while scaling can be challenging. If your team lacks specialized security expertise, consider partnering with professional career services. These services often incorporate enterprise-level protections, such as GDPR and CCPA compliance, automated data retention policies, and clear documentation processes, reducing your risk while ensuring candidate data stays secure throughout the application process.
"Protecting candidate data is not just a legal obligation but also a fundamental aspect of ethical recruitment practices and maintaining trust with clients and candidates." - Matthew Deutsch, Top Echelon
The five strategies outlined here are essential for ATS security, but their success depends on consistent monitoring and updates. Automate where possible, conduct regular reviews, and remember: yesterday’s defenses may not be enough for tomorrow’s threats.
FAQs
How can I verify an ATS vendor’s security claims?
To assess the security claims of an ATS vendor, start by examining their use of encryption to protect sensitive data, their access control measures to restrict unauthorized access, and their adherence to recognized data protection standards. Look into their reputation by reviewing their security practices and any public feedback. It's also a good idea to request certifications or security assessments, such as SOC 2 or ISO 27001, which demonstrate their commitment to safeguarding data. Focus on vendors with clear, transparent policies and a track record of effectively protecting candidate information.
What’s the right data retention period for applicants?
The appropriate length of time to retain applicant data hinges on factors like legal obligations, company policies, and the intended use of the information. Generally, organizations should retain candidate data only for as long as it serves recruitment objectives and adheres to legal requirements. This period often ranges from 6 months to 2 years. Once this timeframe has passed, the data should either be securely deleted or anonymized to ensure the protection of individuals' privacy.
What should an ATS breach response plan include?
An effective ATS breach response plan revolves around four key phases: preparation, detection, containment, and restoration.
- Preparation: This stage involves laying the groundwork by establishing clear policies, assigning specific roles to team members, and safeguarding the ATS with measures like strong access controls and encryption.
- Detection: Early identification is crucial. This includes actively monitoring for any unauthorized access and thoroughly analyzing potential breaches to understand their scope and impact.
- Containment: Once a breach is detected, the priority shifts to halting further data loss. Quick action is essential to minimize the damage and secure the system.
- Restoration: The final step focuses on recovery. This includes notifying all affected parties, restoring compromised data, and revising security protocols to strengthen defenses against future attacks.
By addressing each of these areas, organizations can better manage and mitigate the risks associated with ATS breaches.




