AI Matching vs ATS: Why Resumes Get Rejected
How ATS and AI matching reject 75% of resumes: formatting issues, missing keywords, and biased ranking — plus quick fixes to pass automated screens.

75% of resumes never reach a human recruiter. Why? Most companies rely on Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) or AI Matching tools to screen applications. These systems, while efficient, often reject resumes for reasons like formatting issues, missing keywords, or lack of personalization.
Here’s the key difference: ATS scans for exact keyword matches, while AI Matching analyzes context and ranks candidates based on fit. Yet, both have flaws - ATS is rigid and rejects qualified applicants due to minor inconsistencies, while AI Matching can introduce biases or misinterpret transferable skills.
If you’re applying for full-time jobs, using a job application service, or exploring the best job boards, understanding these systems is critical. Tailored resumes perform better, generating 6 interviews per 100 applications compared to fewer than 3 for generic submissions. Tools like Scale.jobs combine AI with human oversight to help your resume pass these filters and stand out.
Quick Tips to Avoid Rejection:
- Use simple, single-column formats without tables or graphics.
- Include exact job description keywords alongside synonyms.
- Avoid generic, AI-generated resumes - 62% of employers reject them.
Why Your Resume is Rejected by ATS (& How to FIX IT)
How ATS and AI Matching Work
Grasping how these screening systems function is key to navigating them effectively. Both systems aim to filter resumes, but their methods differ significantly - this distinction can determine whether your application reaches a hiring manager or vanishes into the applicant pool. Let’s break down the contrasting approaches of ATS and AI Matching.
What is ATS?
An Applicant Tracking System (ATS) acts like a digital filing cabinet with a built-in filter. Nearly all Fortune 500 companies - around 99% - rely on ATS software and job application tools to organize and sift through the massive influx of applications they receive. These systems scan resumes for specific phrases pulled directly from job postings.
ATS operates using Boolean logic, meaning it looks for exact matches. For instance, a resume mentioning "PMP" could be ignored if the job description specifies "Project Management Professional." Additionally, resumes with unconventional formats - like columns, tables, or intricate designs - often confuse ATS parsers, leading to skipped or misinterpreted information.
The outcome is a binary pass/fail system. your resume either contains the precise keywords in the right structure—often achieved using an AI resume builder—or it doesn’t. There’s no flexibility for related experience or transferable skills. This rigidity explains why 88% of employers feel that highly skilled candidates are sometimes rejected simply because their resumes don’t match the job description word-for-word.
What is AI Matching?
AI Matching systems take a more nuanced approach, going beyond simple keyword matching. Instead of focusing solely on exact phrases, these systems use Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning to understand the context of your resume. They can recognize equivalent terms, such as "customer success" and "client relations", as well as related skills.
AI tools also analyze your entire work history to uncover "Predicted Skills" - abilities you’re likely to have based on your roles, even if they aren’t explicitly listed. These systems can even estimate how many years of experience you have with a particular skill by correlating keyword appearances with dates of employment. Rather than filtering candidates out, the goal of AI Matching is to rank applicants based on the quality of fit with the job.
That said, AI Matching isn’t without flaws. Research has flagged potential biases, such as favoring candidates from prestigious universities or those listed first in a batch of resumes. This "first-position" and "prestige" bias can skew results, sometimes overlooking equally qualified candidates.
Some AI systems go beyond text analysis, incorporating tools like video assessments, gamified tests, and even body-language evaluation. In one notable case, UK makeup artist Anthea Mairoudhiou had to reapply for her own job through HireVue’s AI screening tool. Despite strong skills evaluations, the system flagged her body language during a video interview, which contributed to her termination. Following backlash, HireVue removed its facial analysis feature in 2021.
By offering a deeper evaluation of a candidate’s background, AI Matching directly addresses some of the limitations seen in ATS systems.
| Feature | Traditional ATS | AI Matching Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Logic | Exact keyword matching | Semantic & context analysis |
| Screening Focus | Formatting & hard skills | Transferable skills & "fit" |
| Evaluation Style | Binary (Pass/Fail) | Ranking & scoring |
| Common Weakness | Rejects qualified non-matches | Positional & prestige bias |
| Processing Speed | 30+ minutes for 100 resumes | 2–3 minutes for 100 resumes |
ATS vs. AI Matching: Key Differences
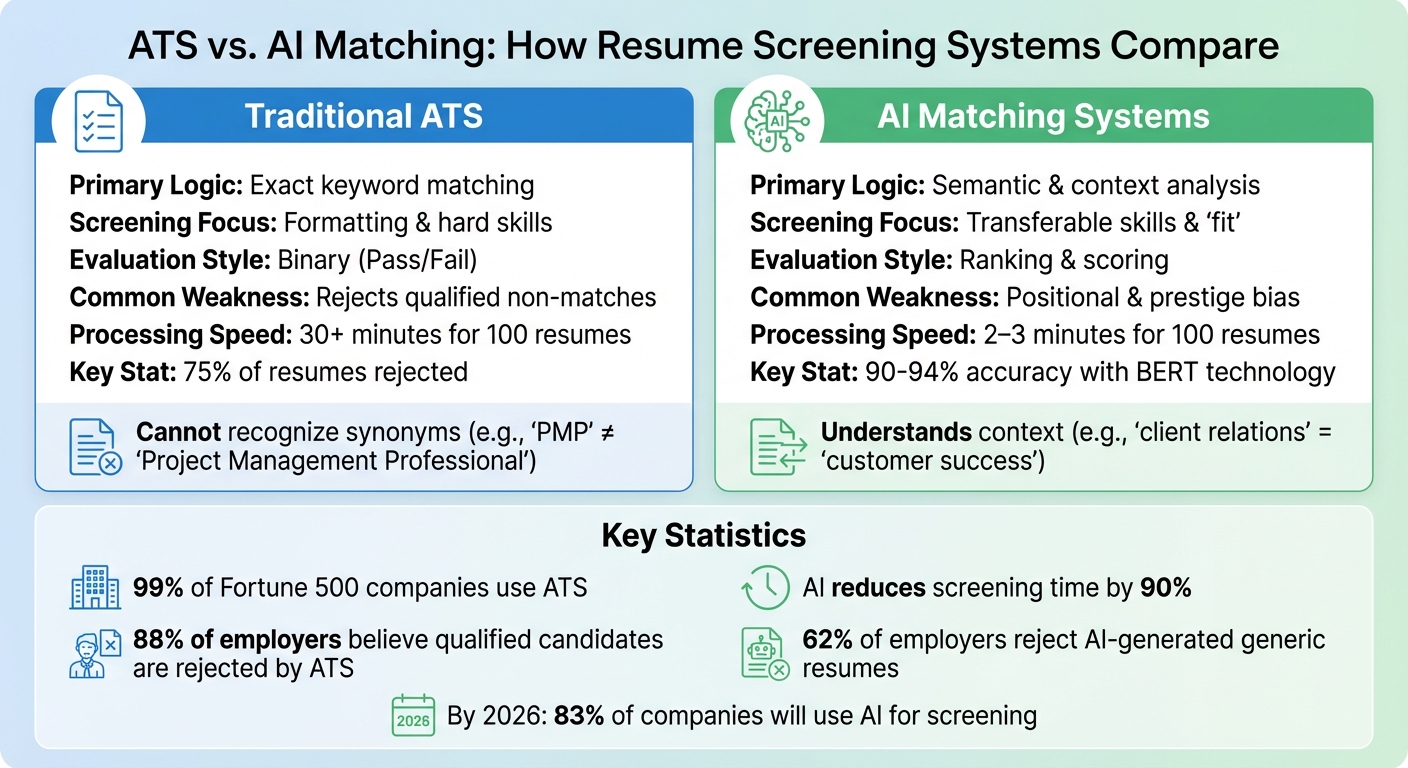
ATS vs AI Matching Systems: Key Differences in Resume Screening
Keyword Matching vs. Context Analysis
Traditional Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) focus on scanning resumes for exact keyword matches from job postings. For example, if your resume says "code developer" but the job description uses "software engineer", the ATS might reject your application - even though the roles are nearly identical. This rigid process filters out about 75% of resumes, often missing qualified candidates who simply use different terms.
AI Matching, on the other hand, takes a more nuanced approach. Leveraging Natural Language Processing (NLP), these systems analyze the meaning behind your words. They understand that terms like "client relations" and "customer success" describe overlapping skills. AI can also infer related competencies - mentioning "Django", for instance, signals expertise in "Python backend development." This contextual understanding addresses one of ATS's major flaws: overlooking candidates who don’t use exact phrasing but are still highly qualified.
"AI doesn't understand context. It doesn't know how you got results or what made your impact unique. Without that, your resume might check all the boxes for keyword searches, but it won't connect with a human reader." - Adam Karpiak, Co-founder, Karpiak Consulting
These differences highlight why AI Matching is more flexible than ATS systems, though both have their own limitations.
Common Rejection Triggers
ATS systems often reject resumes for technical reasons, with formatting issues being a major culprit. Resumes that use multi-column layouts, tables, or graphics can confuse ATS parsers, causing them to skip or misinterpret sections. Additionally, failing to include specific keywords from the job description results in automatic rejection, even if the candidate has the necessary skills under a different name. "Knockout questions" about eligibility - such as work authorization or certifications - can also lead to immediate disqualification.
AI Matching handles these challenges better, as it’s designed to process "messy" or non-standard resumes more effectively. However, it introduces its own set of rejection risks. By 2025, 62% of employers reported rejecting AI-generated resumes that lacked personalization. Hiring managers are increasingly using AI detectors to weed out applications that sound generic or robotic. Additionally, AI systems can introduce positional and fairness biases, which may skew results and inadvertently disadvantage some candidates.
While both systems have their pitfalls, understanding these triggers can help job seekers tailor their applications for better results.
Speed and Accuracy Comparison
The speed and accuracy of these systems play a critical role in how applications are screened. AI-powered tools can reduce candidate screening time by up to 90%, saving recruiters an average of 10+ hours per role. For instance, Unilever reported in 2019 that automated screening saved them 100,000 hours and nearly $1 million in recruitment costs. Companies using AI solutions also see a 25% reduction in the time it takes to fill positions.
When it comes to accuracy, AI Matching significantly outperforms traditional ATS systems. Models enhanced with BERT technology achieve 90–94% accuracy in matching candidates to job descriptions, far surpassing the basic keyword matching of ATS. However, no system is perfect. While ATS often creates "false rejections" by overlooking qualified candidates due to rigid keyword requirements, AI Matching can introduce biases that affect its rankings. The key difference lies in their approach: ATS functions as a binary gatekeeper, rejecting or accepting candidates outright, whereas AI evaluates and ranks candidates based on their fit. Both systems improve efficiency, but human oversight remains essential to address biases and ensure fair assessments.
Why ATS Rejects Resumes
Exact Keyword Requirements
ATS platforms often rely on rigid keyword matching, which can lead to the rejection of highly qualified candidates. These systems operate on a strict checklist, dismissing resumes that don't include exact phrases from the job posting.
"AI is too stupid to recognize transferrable skills among tech applicants... I had a resume bounced because I don't have c# listed as a fluent language, even though I've dealt with c# in my jobs." - Josh Holbrook, Software Engineer
Essentially, ATS systems lack the ability to interpret synonyms or context. They scan resumes for precise word matches, which explains why 88% of employers believe qualified candidates are filtered out due to mismatched terminology. This issue is especially problematic in technical roles, where minor differences in phrasing can overshadow relevant experience. AI Matching systems, however, use Natural Language Processing to identify semantic similarities, bridging the gap between different terminologies and improving the accuracy of candidate evaluations.
Missing Context and Skills Analysis
Another major limitation of ATS platforms is their inability to assess the depth and relevance of a candidate's experience. These systems simply check for the presence of keywords without considering how they are applied. For instance, a candidate with extensive leadership experience might be viewed the same as someone who briefly mentions a skill in passing. Important factors like career progression, the quality of prior employers, and demonstrated expertise are often overlooked.
"The danger is when companies start treating hiring like a data problem instead of a people problem, even as job search automation becomes more common." - Adam Karpiak, Co-founder, Karpiak Consulting
This lack of context highlights why AI Matching systems are more effective. Unlike traditional ATS platforms, these systems analyze the relevance and depth of past roles, offering a more comprehensive understanding of a candidate's qualifications and experience.
File Format and Design Problems
Resume formatting is another common hurdle with ATS platforms. Many systems, such as Lever, struggle to accurately parse resumes that include columns, tables, or graphics, leading to the rejection of qualified applicants.
"Lever cannot accurately parse the information inside columns or tables. Keep your formatting simple and avoid columns or tables so that your resume is easy to reach and searchable." - Steph Cartwright, Certified Resume Writer
To avoid these issues, submit resumes in .docx or .doc formats with a straightforward, single-column layout. Use PDFs only if specifically requested. Additionally, include both abbreviations and their full terms (e.g., "PMP" alongside "Project Management Professional") to ensure your qualifications are fully recognized. AI Matching systems offer a significant advantage here, as they can process a variety of resume formats and extract meaningful information from unstructured layouts. These technical limitations of ATS platforms explain why so many resumes fail to move past the initial screening stage.
Why Scale.jobs Beats ATS-Only Tools
Tackling the shortcomings of ATS-only tools, Scale.jobs offers a more holistic approach by combining technical precision with personalized recruitment strategies.
Human + AI Combined System
While tools like Jobscan and TealHQ rely solely on automated keyword matching, Scale.jobs takes it a step further by integrating AI with human expertise. Real people review and refine your resumes and cover letters, ensuring they are polished and tailored. They also handle applications, providing real-time WhatsApp updates and time-stamped proof-of-work screenshots. This blend of human and AI ensures that your application not only passes ATS filters but also connects on a more personal level - something purely automated systems often fail to achieve. This thoughtful approach lays the groundwork for additional benefits in pricing and support.
Transparent, Flat-Fee Pricing
Scale.jobs operates on a simple, flat-fee structure - $199 for 250 applications - with no hidden costs or recurring subscriptions. This straightforward pricing beats competitors like Rezi.ai and TopResume, which rely on costly monthly plans. Plus, unused credits are refundable, offering flexibility and peace of mind. Combined with its enhanced screening process, Scale.jobs directly addresses the inefficiencies of ATS systems without breaking the bank.
Free Job Search Tools
Scale.jobs goes beyond the basics by offering a suite of free tools to streamline your job hunt. These include an ATS resume checker, cover letter generator, application tracker, salary predictor, and interview question predictor - all available without the subscription fees charged by platforms like Jobscan. Additionally, the platform provides an ATS-friendly resume builder and portfolio website generator at no cost, helping users overcome formatting issues that could lead to ATS rejections.
Visa and Immigration Support
One of Scale.jobs' standout features is its support for visa and immigration challenges, such as H1B, F1, CPT, TN, and O1. Unlike tools like TealHQ or LoopCV, Scale.jobs employs human experts to craft applications that address work authorization questions. This is critical, as 98.8% of Fortune 500 companies use ATS systems featuring "knock-out" questions about work eligibility. By navigating these fields with care, Scale.jobs significantly improves your chances of moving past initial screenings and securing callbacks.
Conclusion
Did you know that up to 75% of resumes are rejected by ATS tools due to simple formatting mistakes or missing keywords? That’s where AI Matching steps in, leveraging Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand context and meaning, rather than just scanning for keywords. Companies adopting a hybrid approach - combining AI technology with human oversight - have reported impressive results: a 40% drop in hiring bias and a 30% improvement in hiring efficiency.
Looking ahead, by 2026, 83% of companies are expected to use AI for resume screening. But as career coach Bob Dichter wisely points out:
"You need a human in the loop to use the AI appropriately and you need great set of instructions and very pertinent source materials to create the right resume for the right job."
This highlights the importance of blending AI's speed with human intuition. Scale.jobs exemplifies this balance. Unlike competitors like Jobscan and TealHQ, which focus heavily on keyword optimization, Scale.jobs takes it a step further. Their trained virtual assistants manually review and manage each application, ensuring no parsing errors or formatting issues slip through the cracks. With a clear flat-fee model starting at $199 for 250 applications, Scale.jobs offers the precision of AI combined with the care of human expertise - a combination 62% of employers prefer.
This hybrid strategy doesn’t just help you pass ATS filters - it gives you a real shot at landing interviews.
FAQs
How can I make my resume stand out to both ATS and AI-powered job matching systems?
To make your resume stand out in both ATS and AI-driven job matching systems, focus on integrating key terms directly from the job description that reflect the role's requirements. Customizing your resume for each job application ensures your skills and experience align with what employers are seeking.
Stick to a straightforward and clean layout. Avoid using graphics, images, or intricate designs, as these can confuse ATS scanners. Opt for standard fonts, clear section headings, and bullet points to enhance readability.
To fine-tune your resume, you might want to explore tools designed to assess ATS compatibility and optimize keywords. These tools can help highlight areas for improvement, increasing your chances of catching a recruiter’s attention.
Why do resumes often get rejected by ATS systems?
Resumes often get rejected by Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) because they miss key job-related terms, use poorly structured formatting, or don’t align with the specific criteria outlined in the job posting. These systems are programmed to sift through applications and eliminate those that don’t meet the set standards, meaning your resume might never reach a recruiter’s desk.
To enhance your chances of success, make sure your resume is ATS-friendly. Use simple, clean formatting, incorporate relevant industry keywords, and customize it to fit the job description. Platforms such as AI-powered resume builders can assist in fine-tuning your resume, giving it a better shot at clearing the ATS screening and landing in front of a hiring manager.
How does AI-powered job matching improve on traditional ATS systems?
AI-driven job matching systems take hiring to the next level by addressing the shortcomings of traditional applicant tracking systems (ATS). While ATS often depends on strict keyword matching, these advanced systems use artificial intelligence to evaluate resumes and job descriptions with a deeper understanding. This means they can more accurately identify skills, experience, and overall fit, ensuring qualified candidates don’t slip through the cracks.
Beyond improving accuracy, these systems handle repetitive tasks automatically, saving valuable time for both recruiters and job seekers. They also contribute to fairer hiring practices by relying on data-driven insights rather than subjective opinions, helping to reduce unconscious bias and create a more inclusive recruitment process.




